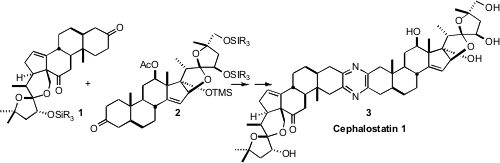
The cephalostatins and ritterazines, represented by Cephalostatin 1 (3),
have the remarkable property of inducing apoptosis in apoptosis-resistant
malignant cell lines. Methyl 2-formyl-4-hydroxybenzoate manufacturer The total synthesis
(J. Am. Chem. PMID:24507727 Soc. 2010, 132, 275.
DOI: 10.1021/ja906996c)
of 3 by Matthew D. 3-Butynoic acid Chemical name Shair of Harvard University required the practical
preparation of the complex
hexacyclic ketones 1 and 2.
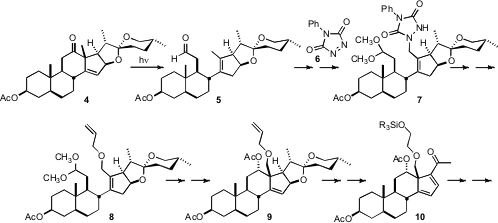
The preparation of 1 started with irradiation of commercial hecogenin acetate
4 to give the known aldehyde 5. Reaction of 5 with N-phenyltriazolenedione
(6) led
to the ketal 7. Oxidative cleavage generated an aldehyde, that on reduction and
allylation was converted to 8. Acid-mediated cyclization led to 9.
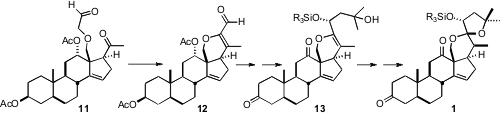
The sidechain of 9 was removed, giving 10, that was selectively reduced,
leading to 11. Intramolecular aldol condensation gave 12. The relative
configuration of the spiroketal 1 was established by kinetic bromoetherification
of the alcohol 13, followed by free radical reduction of the resulting tertiary
bromide, and acid-catalyzed equilibration.
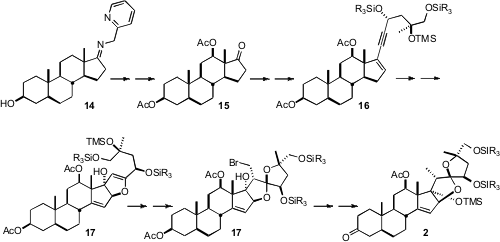
The synthesis of 2 began with the inexpensive steroid 14. Following the
Schönecker protocol, C-H functionalization led to the ketone 15. Pd-mediated
coupling of the derived enol triflate with the alkyne gave 16, that was oxidized
and cyclized to 17. Simmons-Smith conditions converted the dihydrofuran of
17 into the cyclopropane, that was again opened kinetically with bromine (NBS) to set the relative configuration of the spiroketal. Free radical reduction
followed by protection and oxidation then completed the preparation of 2.
The coupling of 1 and 2 (not illustrated) to form the central pyrazine of
3 followed the precedent of Fuchs, combining the 2-azido ketone derived from
1 with the 2-amino methoxime derived from 2. Remarkably, tens of milligrams of
1
and of 2 were prepared, assuring a reasonable supply of 3 for further studies.