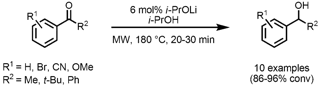
The group of Hans Adolfsson from Stockholm University has shown that ketones can be reduced to the corresponding alcohols via transfer hydrogenation in the absence of a transition metal catalyst when catalytic amounts of an alkali alkoxide are employed (Adv. Synth. Catal. 2007, 349, 1609. DOI: 10.1002/adsc.200700091). The reaction proceeded smoothly for a range of aromatic and aliphatic ketones using lithium isopropoxide (i-PrOLi) as catalyst and i-PrOH as hydrogen donor. Problematic ketone substrates, e.g. 2-Chloro-3-methoxypyridin-4-amine site where R1 = CN or acetylpyridines that show coordination to the metal catalyst under traditional conditions can be converted to the alcohols in high yields. PMID:34856019 In addition, a scale-up from 0.5 mmol to 82 mmol for acetophenone (R1 = H, R2 = Me) was conducted employing a multimode instrument under the same reaction conditions giving the alcohol in similar isolated yield.
Synthesis of β-Amino Alcohols
The groups of Domingo Gomez Pardo and Janine Cossy from ESPCI-ParisTech, France, were successful in the stereoselective rearrangement of β-amino alcohols via an aziridinium intermediate under catalytic conditions (J. 1-(2-Aminoethyl)piperidin-4-ol Data Sheet Org. Chem. 2007, 72, 6556. DOI: 10.1021/jo071028x). Linear N,N-dibenzyl β-amino alcohols1 and N-benzyl prolinol (2) rearranged to β-amino alcohols 3 and 3-hydroxypiperidine (4), respectively, by treatment with 0.2 equiv of trifluoroacetic anhydride followed by saponification with 0.3 equiv of NaOH in high yields and excellent ee´s. Compared to the traditional method where stoichiometric amounts are employed, Et3N can be omitted from the procedure.

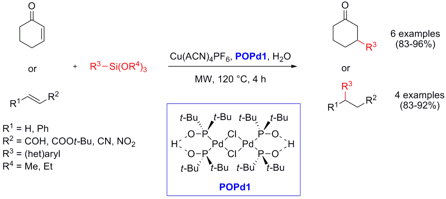
Palladium(II)-Catalyzed Conjugate Additions
Christian Wolf and Rachel Lerebours from Georgetown University, Washington, have reported on the palladium-phosphinous acid catalyzed conjugate addition of (het)aryl siloxanes to α,β-unsaturated substrates in water (Org. Lett. 2007, 9, 2737. DOI: 10.1021/ol071067v). Key to the success of a general method is the employment of 10 mol% of a copper co-catalyst (Cu(ACN)4PF6) additional to 5 mol% of the palladium catalyst POPd1. An advantage of the palladium-phosphinous acid catalystPOPd1 is the air and water stability that eliminates an inert atmosphere during the reaction. With this protocol, β-substituted ketones, aldehydes and nitroalkanes were obtained in high yields. Even otherwise difficult available β-substituted esters and nitriles can be generated smoothly in this way.
Dihydroquinoline and Quinoline Synthesis via Tandem Hydroamination-Hydroarylation
Chi-Ming Che and co-workers from the University of Hong Kong have developed a method for the synthesis of substituted1,2-dihydroquinolines and quinolines under gold-catalysis (Org. Lett. 2007, 9, 2645. DOI: 10.1021/ol070814l). The reaction of anilines1 with alkynes 2 employing the Au(I) catalyst3/AgOTf combination afforded the corresponding dihydroquinolines 4 via a tandem hydroamination-hydroarylation sequence. By utilizing the proper substituted alkynes 2, products containing multiple alkyne groups can be obtained as well. Under similar conditions, quinolines 6 can be synthesized when alkynes are reacted with o-acetyl or -benzoyl substituted anilines 5.
