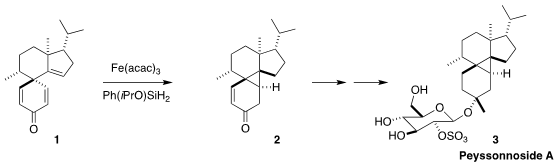
Peyssonnoside A (3), isolated from the red alga Peyssonnelia
sp., shows promising anti-microbial activity. PMID:24275718 Mingji Dai of Emory University
assembled the tetracyclic core of 3 by the H-atom transfer cyclization of
the dienone 1 to the
cyclopropane 2
(J. Am. Palladium (II) acetate site Chem Soc. 5-Bromo-3-fluoro-2-nitropyridine site 2022, 144, 19700.
DOI: 10.1021/jacs.2c09919).
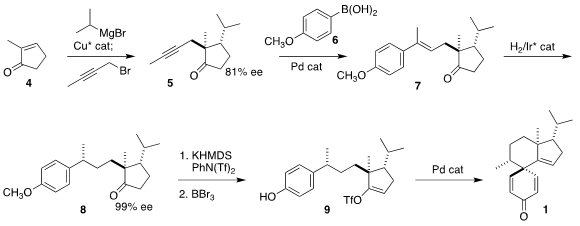
The starting material for the preparation of 1 was commercial 2-methyl
cyclopentenone (4). Following the Alexakis protocol,
conjugate addition
with isopropyl magnesium bromide followed by trapping of the enolate so produced
with 1-bromo-2-butyne led to the ketone 5 in 81% ee. Coupling with the
boronic acid 6 proceeded with high regio and geometric control, to give
7. Enantioselective
hydrogenation then delivered 8 in high ee, along with a minor amount
of the other diastereomer, that was removed. Enol triflate formation and
demethylation then set the
stage for Pd-catalyzed cyclization to 1.
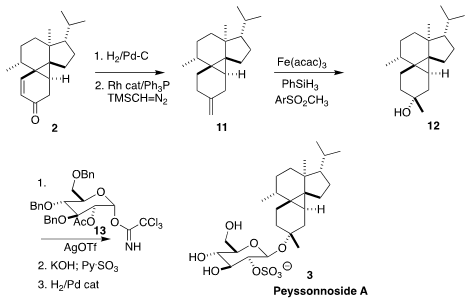
The H-atom mediated cyclization of 1 proceeded smoothly to give the
tetracylic 2. The reaction is probably proceeding by H atom addition to
the trisubstituted alkene, to give an intermediate radical that adds to the
accesible face of the dienone.
Hydrogenation of 2 led to the saturated ketone, that initially
resisted
methylenation. Here the Lebel protocol proved useful, delivering 11, that was hydrated to give 12.
At this point the synthesis converged with the alternative total synthesis of
peyssonnoside A (3) reported by Karl Gademann of the University of Zurich
(J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 14083.
DOI: 10.1021/jacs.1c07135),
concluding by coupling with 13 to give 3.