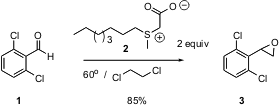
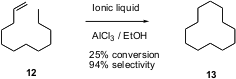The development of new methods for carbon-carbon bond formation is at the heart of organic synthesis. 2-(Difluoromethyl)pyridin-4-amine Data Sheet The most desirable methods are those that are easily practiced at scale, operate near ambient temperature, and that do not require strong acid or base. 5-Formylnicotinic acid structure David C. Forbes of the University of South Alabama and Michael C. Standen of Synthetech in Albany, OR report (Org. Lett. 2003, 5, 2283.DOI: 10.1021/ol034612a)that the crystalline salt2, which can be stored, smoothly convertsaldehydes to epoxides, without any additional added base. PMID:23892746 The reaction is apparently proceeding by the loss of CO2 from 2 to give the intermediate sulfonium methylide.
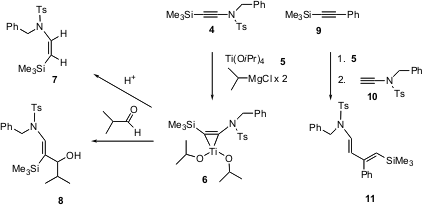
Fumie Sato of the Tokyo Institute of Technology has extensively developed applications of titanacyclopropenes such as6. He now reports (Org. Lett. 2003, 5, 67.DOI: 10.1021/ol027209x)the extension of this work to ynamides such as 4 and 10. The titanacycle 6 derived from 4 can be protonated to give the cis alkene7. Titanacycle 6 also adds to an aldehyde, to give the geometrically-defined allylic alcohol8. Alternatively, the titanacycle prepared from another alkyne such as 9 will add to the ynamide10, to give the diene 11. Titanium isopropoxide and 2-propylmagnesium chloride are inexpensive, and these couplings do not require catalysis by other transition metals.
Usually, the construction of carbocyclic rings requires the preparation of highly functionalized intermediates. Youquan Deng of the Lanzhou Institute of Chemical Physics reports (Tetrahedron Lett. 2003, 44, 2191.DOI: 10.1016/S0040-4039(03)00158-8)that simple acid-mediated equilibration of 1-dodecene 12 gives a remarkably efficient conversion to cyclododecane 13. The authors speculate that the peculiar thermodynamic stability of 13 favors this transformation.