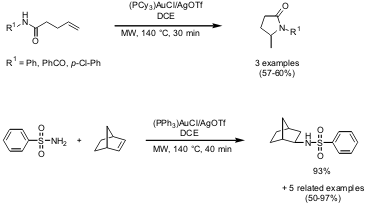
Chi-Ming Che and co-workers from the University of Hong Kong have reported on the intra- and intermolecular hydroamination of unactivated alkenes (Org. Lett. 2006, 8, ASAP. DOI: 10.1021/ol060719x). In a catalyst screening the phosphine gold(I) catalyst combinations (PCy3)AuCl/AgOTf and (PPh3)AuCl/AgOTf, respectively, showed the best catalytic activity. By applying microwave heating not only were reaction times reduced (e.g. 578729-05-2 Purity 30 h → 30 min) but also the amount of catalyst, compared to conventional heating. Formula of 887144-94-7
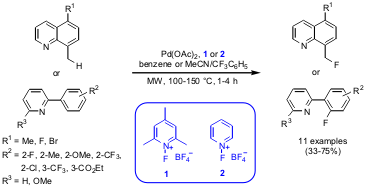
Pd-Catalyzed C-F-Couplings
A new protocol for the Pd-catalyzed fluorination of C-H bonds was developed by the group of Melanie S. Sanford at the University of Michigan (J. PMID:24238415 Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 7134.DOI: 10.1021/ja061943k). This reaction proceeds via a Pd(OAc)2-catalyzed C-H activation/oxidative fluorination step where an electrophilic fluorinating reagent (1 or 2) is necessary for successful aromatic and benzylic C-F bond formations. Compared to thermal heating, higher yields could be achieved with microwave irradiation due to shorter reaction times.
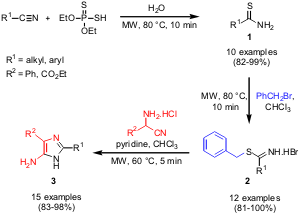
Parallel Synthesis of 2,4-Disubstitued 5-Aminoimidazoles
Comparison studies of thermal vs. microwave heating in the synthesis of 2,4-disubstituted 5-aminoimidazoles 3 have been conducted by Yulin Lam and co-workers from National University of Singapore (J. Comb. Chem. 2006,8, ASAP. DOI: 10.1021/cc060030j). Higher yields and considerable rate enhancements (up to ca. 130 times for the overall reaction) could be achieved by applying microwave heating for all three synthetic steps. The synthesis of 5-aminoimidazole scaffolds 3 was performed in parallel employing a multivessel rotor system, making the protocol amenable for high-throughput synthesis.
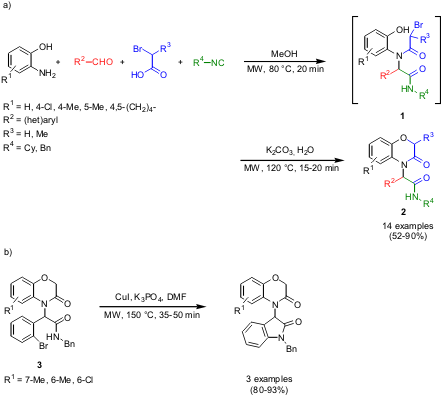
One-Pot Ugi Four-Component Reaction and Intramolecular O-Alkylation
The synthesis of 3,4-dihydro-3-oxo-2H-1,4-benzoxazines 2 was disclosed by the group of Wei-Min Dai at Zhejiang University, China (Tetrahedron 2006, 62, 6774. DOI: 10.1016/j.tet.2006.05.001). Highly functionalized benzoxazine derivatives2 were obtained via a one-potUgi four-component reaction of 2-aminophenols, aromatic aldehydes, α-bromoalkanoic acids and isocyanides and subsequent base catalyzed O-alkylation of 1. By additional post-modification of scaffolds 3 through CuI-catalyzed intramolecular amidations, a novel class of heterocyclic derivatives could be achieved.