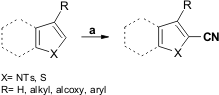Weaker and longer than covalent linkages, hypervalent bonds are the result of a linear three-center, four-electron (3c-4e) electronic distribution (hypervalent model). PMID:23927631
Hypervalent iodine reagents are useful synthetic tools due to their low toxicity, ready availability, and ease of handling. This review focuses only recent advances in this field, from 2004 to present; excellent reviews can be found for previous work (Chem. Rev. 1996, 96, 1123.DOI: 10.1021/cr940424+; Pure Appl. Chem. 1996, 68, 627-630. link;Hypervalent Iodine in Organic Synthesis, Academic Press: San Diego, 1997; Org. Prep. Proc. Int. Formula of 3-Bromopyridazine 1997, 29, 409; Chemistry in Hypervalent Compounds, Wiley-VCH: New York,1999; Synthesis 1999, 1271. DOI: 10.1055/s-1999-3540;Chem. Rev. 2002, 102, 2523.DOI: 10.1021/cr010003+; Hypervalent Iodine Chemistry; Springer: Berlin, 2003). During the preparation of this paper an interesting perspective was published (J. Org. Chem. 2005,70, 2893. DOI: 10.1021/jo050117b).
1. Hypervalent(III) iodine reagents – Iodanes
1.1 Diaryliodonium salts
These compounds are considered ionic, despite their T-shaped pseudo tetrahedral geometry centered in the iodine atom.
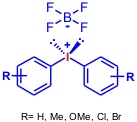
Chen and co-workers report a selective copper-catalyzed mono- and diarylation protocol using diaryliodonium salts. 2410440-12-7 web Using different bases compounds 2 and3 are selectively obtained (K2CO3: 5% of 2 and 59% of 3; NaOAc: 59% of2 and traces of3). The authors use this methodology to synthesize diaryl (4, 52-85% yield) and monoaryl (5, 40-60 % yield) derivatives of uracil and thymine (Helv. Chim. Acta,2005, 88, 290.DOI: 10.1002/hlca.200590010).
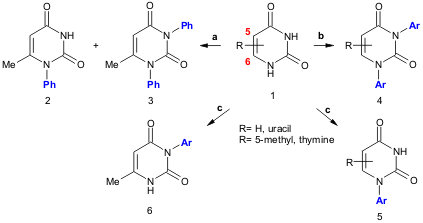
a) 1 (1.0 mmol), Ph2I+BF4–(1 mmol), CuI (10 mol%), base (2.0 mmol), DMF (5 ml), 40 ºC, 6h; b) 1 (0.5 mmol), Ar2I+BF4– (1.2 mmol), CuI (10 mol%), K2CO3 (2.0 mmol), DMF (5 ml), 40 ºC, 3-4h,; Ar = Ph, 4-Me-C6H4, 4-Cl-C6H4, 4-Br-C6H4; c) 1 (1.0 mmol), Ar2I+BF4–(1.2 mmol), CuI (10 mol%), NaOAc (2.0 mmol), DMF (5 ml), 40 ºC, 10h; Ar = Ph, 4-Me-C6H4, 4-OMe-C6H4, 4-Cl-C6H4, 4-Br-C6H4.
1.2 PhIX2 reagents
Compounds of this type exhibit a T-shaped distorted trigonal bipyramidal geometry with the more electropositive substituent and the nonbonding electron pairs on the iodine in the equatorial positions. The axial substituents have a collinear arrangement and share their interaction with the same iodine orbitals, mainly the iodine pz orbital and s orbital, resulting in a “hypervalent trans effect” (ARKIVOK, 2005, (iv), 19.link).
PIFA and PIDA reagents
PIFA (phenyliodine bis(trifluoroacetate)) can serve as an oxidant similarly to Tl(III), Hg(II), and Pb(IV), while being less toxic than these heavy metal containing reagents.
Kita and co-workers report the regioselective PIFA-mediated cyanation of electron-rich heteroaromatic compounds under mild conditions via an SET (single electron transfer) mechanism. The aromatic cation radical intermediate formed reacts with the cyanide anion by a one-electron oxidation followed by deprotonation. The 2-cyano derivatives of pyrrole (43-97% yield), indole (37-62% yield), and thiophene (42-79% yield) were obtained using this cyanation protocol. The protecting group on nitrogen was shown to be crucial, with tosyl derivates being the most reactive. Poor results were obtained using other hypervalent iodine reagents, such as PIDA (phenyliodine diacetate) or HTIB (hydroxy(tosyloxy)iodobenzene) (Org. Lett. 2005, 7, 537.DOI: 10.1021/ol0476826).
a) PIFA (2.0 mmol), BF3.Et2O (4.0 mmol), TMSCN (3.0 mmol), CH2Cl2, rt, 3 h.
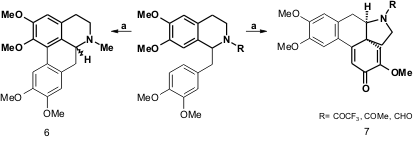
Lee and co-workers also report an intramolecular oxidative coupling via an SET mechanism using PIFA (Helv. Chim. Acta 2004, 87, 167.DOI: 10.1002/hlca.200490005). This approach was used to synthesize (±)-glaucine (6) (33% yield) and (±)-neospirodienones (7) (42-70% yield).
a) PIFA (1.12 eq.), BF3.Et2O (2.62 eq.), CH2Cl2, -40 ºC, 3 h.
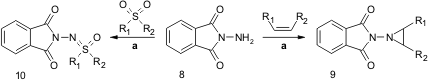
Yudin and co-workers found that whenPIDA is used as a mild oxidant in the presence of N-aminophthalimide 8, a nitrene transfer to olefins and sulfoxides occurs giving aziridines 9 and sulfoximines 10, in moderate to high isolated yields and with high selectivity. The reaction conditions tolerate a wide range of functional groups (ARKIVOC 2005, (iv), 26.link).
a) PIDA (1.5 eq.), olefin or sulfoxide (1.0 eq.), PhthNH2 (2.0 eq.), CH2Cl2, rt, 3-4 h.
Koser’s reagent and IBA derivatives
Wirth and Yusubov published a solvent-free procedure for the synthesis of hypervalent iodine reagents 11 (Koser’s reagent derivatives) and 12 (IBA derivatives) (Org. Lett. 2005, 7, 519.DOI: 10.1021/ol047363e)
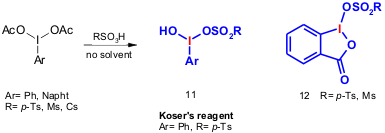
p-Ts = 4-Me-C6H4SO2; Ms = MeSO2; Cs = (1R)-10-camphorylsulfonyl, IBA = iodosyl benzoic acid
Ion-supported reagents
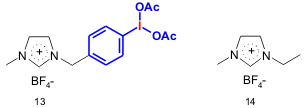
Zhang and co-workers found that [dibmim][BF4] (13) can be used for the selective oxidation of primary (57-95% yield) and secondary (75-98% yield) alcohols to aldehydes and ketones, respectively, without further oxidation to carboxylic acids using [emim][BF4] (14) as a solvent Poor yields were obtained under the same conditions when PhI(OAc)2 was used (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005,44, 952.DOI: 10.1002/anie.200461889).
a) alcohol (0.5 mmol), [dibmim][BF4] (0.7 mmol), [emim][BF4] (1.5 g), NaBr 2 % (w/w), 30 ºC, 3-18 h. [dibmim][BF4] = 1-(4-diacetoxyiodobenzyl)-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate; [emim][BF4] = 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate
2. Hypervalent(V) iodine reagents – Periodanes
IBX reagent
Iodine(V) reagents are shock and pressure sensitive. Explosions ofo-iodoxybenzoic acid (IBX, 15) can occur at temperatures above 200 ºC.
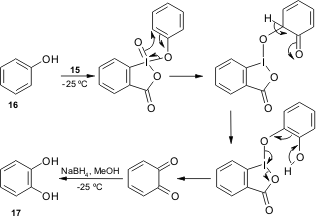
A regioselective oxidation of phenols to o-quinones usingIBX was recently reported by Pettus and co-workers (Org. Lett. 2002, 4, 285.DOI: 10.1021/ol017068j). D’Ischia and co-workers have now expanded the scope of this method to estrogens and several other phenolic compounds using a low temperature reductive procedure under homogeneous phase conditions (Tetrahedron Lett. 2005, 46, 3541.DOI: 10.1016/j.tetlet.2005.03.060).
Scheme 1. Mechanism of the IBX-induced conversion of phenol (16) to catechol (17).