The tetraketone aberrarone (3), isolated from the feathery Caribbean gorgonian
Pseudopterogorgia elisabethae, shows in vitro activity against the malaria
parasite. Yanxing Jia of Peking University devised a route to 3 based on the
oxidative radical cyclization of 1 to 2
(J. Am. Chem. Soc. PMID:25269910 EPhos Pd G4 Data Sheet 2023, 145, 9459.
DOI: 10.1021/jacs.3c02511). 3-(4-Bromophenyl)oxetan-3-ol Formula
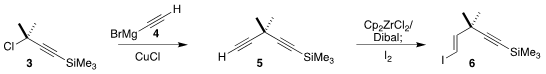
The eneyne sidechain of 1 was prepared from the commercial chloride 3. Cu-catalyzed coupling with the Grignard reagent
4 led to the diyne 5.
Hydrozirconation followed by iodination then gave 6.
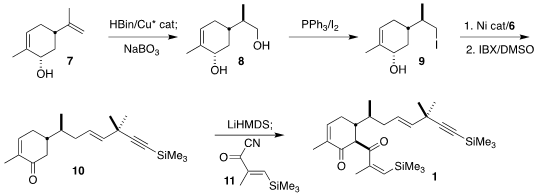
The synthesis began with commercial (S,S)-carveol (7). Diastereoselective
hydroboration led to the diol 8, that was selectively
converted to the iodide
9. Remarkably, direct coupling of 9 with the alkenyl iodide 6 followed by
oxidation led cleanly to the desired 10.
Acylation with 11 then completed the assembly of
1.
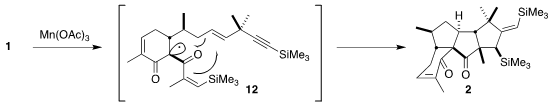
Oxidation of the 1,3-diketone 1 with
Mn(OAc)3 would initially give the
radical 12. The cascade radical cyclization followed, leading with high
diastereocontrol to the tetracyclic ketone 2.
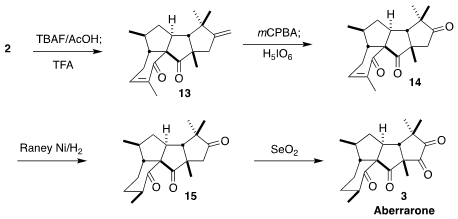
Desilylation of the diketone 2 gave the diene 13. Selective
epoxidation followed by periodate cleavage led to the triketone 14.
Hydrogenation gave
15,
that was oxidized to the tetraketone aberrarone (3).
It is instructive to compare this synthesis with that reported by Carreira.