The diterpenoid cephinoid H (3), isolated from methanolic extracts of
Cephalotaxus fortunei var. alpina, a conifer of Southwest China,
showed remarkable anti-cancer activity. [Ir[dF(CF3)2ppy]2(bpy)]PF6 manufacturer Xiangdong Hu of Northwest University
constructed the tropolone of 3, essential to anti-cancer activity, by
ring-closing metathesis of 1, followed by elimination to give 2
(Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 18572,
DOI: 10.1002/anie.202108034;
Eur. PMID:34856019 1355070-36-8 Chemical name J. Org. Chem. 2022, e202101430,
DOI: 10.1002/ejoc.202101430).
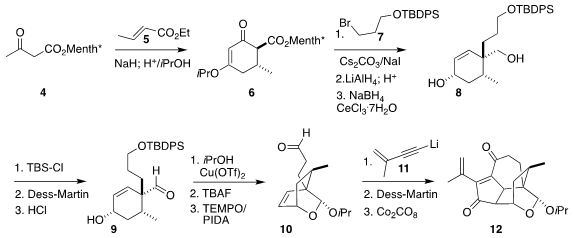
The absolute configuration of 1 was set following the Myers protocol,
Michael addition of menthyl acetoacetate 4 to ethyl crotonate 5,
followed by cyclization, leading to 6. Alkylation with 7 and
subsequent reduction delivered 8, that was carried on to the aldehyde
9. Hemiacetal formation followed by deprotection and oxidation led to 10,
setting the stage, via the addition of the alkynyl lithium 11, for
Pauson-Khand cyclization to the enone 12.
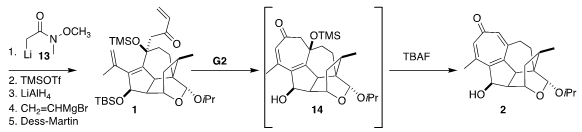
The addition of the Weinreb amide 13 to 12 set the stage for
subsequent direct
LiAlH4 reduction to the intermediate aldehyde,
allowing facile construction of the enone 1. Ring-closing metathesis led
to the unstable cycloheptadienone 14, that on exposure to TBAF was
converted to the desired tropolone 2.
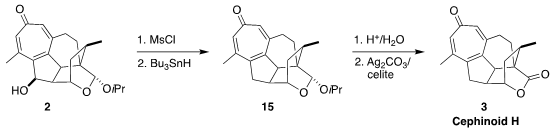
The alcohol 2 served as a versatile branch point leading to the
synthesis of several of the Cephalotaxus diterpenoids. For cephinoid H (3),
exposure of the alcohol to MsCl delivered the chloride, that was reduced under
free radical conditions. Hydrolysis of the hemiacetal followed by oxidation then
completed the assembly of 3.
It is instructive to compare this approach to the syntheses of the related
cephanolide A described by Gao (OHL 20210802) and by Sarpong (OHL20211220).
It is instructive to compare this approach to the syntheses the related
cephanolide A described by Gao
(![]() 2021, August 2)
2021, August 2)
and Sarpong (![]() 2021,
2021,
December 20).